Forensic company who helped police crack Gilmour, Tice cases reveals how they did it
The company that helped the Toronto police crack a decades-old cold case is revealing more details about how they identified a suspect in the grisly murders of two Toronto women in 1983.
Othram Inc., a Texas-based lab that leverages forensic genealogy to solve cold cases, was a crucial piece in helping investigators identify Joseph George Sutherland.
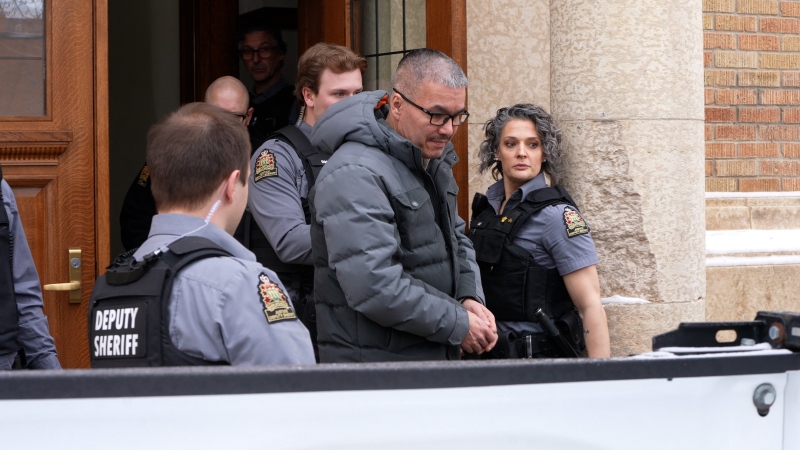
On Monday, Toronto police announced that they had arrested the 61-year-old in connection with the murders of two Toronto women in 1983, Erin Gilmour and Susan Tice.
Othram’s Chief Development Officer, Kristen Mittleman, told CTV News Toronto that Toronto police handed their team a piece of evidence after the force exhausted standard forensic testing and found no matches.
“Our DNA testing is something that no one else on earth can do right now the way that we do it here at Othram. We are the first lab that's purpose-built to take this type of evidence and use it for this really advanced forensic genome sequencing process,” Mittleman said.
It’s Othram’s job to then determine if the DNA picked up from the evidence is sufficient to sequence, she said.
“I believe that this [DNA sample] was a sperm fraction,” Mittleman said, noting that their team discovered a “mixture” of DNA samples from the “perpetrator and victim” in this particular cold case.
 An image of Joseph George Sutherland. (Facebook/Joseph G. Sutherland)In the “exact same manner” Mittleman said they worked with the Toronto police to uncover the man responsible for the murder of nine-year-old Christine Jessop who was sexually assaulted and killed more than 35 years ago.
An image of Joseph George Sutherland. (Facebook/Joseph G. Sutherland)In the “exact same manner” Mittleman said they worked with the Toronto police to uncover the man responsible for the murder of nine-year-old Christine Jessop who was sexually assaulted and killed more than 35 years ago.
Though Othram did not work on the infamous Golden State Killer case involving the former California police officer who raped and murdered dozens of victims in the 1970s and 80s, Mittleman said the same technology was used.
She said the key difference between the Sutherland and the Golden State Killer case was that the latter had “multiple victims and a ton of DNA,” whereas the Toronto cold case had a “very small” and “intractable” sample.
Once Othram processed the DNA, they gave it to a genealogist at the Toronto Police Service who uploaded it to a genealogical database to cross reference with genetic information of the suspect’s relatives and eventually zero in on Sutherland.
“They were able to take all those matches and work back through the genealogical tree until they came to the identity of the perpetrator,” Mittleman said.
 Joseph George Sutherland, 61, of Moosonee, was arrested on Thursday. (Supplied)“They use our result as an investigative lead to go investigate the case, figure out if that person was someone that could have been in the area at the time, fit the description of what happened, and then they do standard forensic testing again, to confirm the result.”
Joseph George Sutherland, 61, of Moosonee, was arrested on Thursday. (Supplied)“They use our result as an investigative lead to go investigate the case, figure out if that person was someone that could have been in the area at the time, fit the description of what happened, and then they do standard forensic testing again, to confirm the result.”
When Othram launched, Mittleman said they were solving multiple cold cases over the course of a year. But now, she said they are working on multiple cases a week with the hope of that eventually surging to multiple cases an hour.
“I think that cold cases will be extinct within the next decade,” she said.
“People won't have to wait decades to find out what happened to their loved one. I really do believe that perpetrators are going to start getting caught the first time they commit a crime, rather than having to wait till the second, third, fourth, or whenever they get caught. I also believe that that's going to start becoming a deterrent for crime.”
CTVNews.ca Top Stories

What to know about avian influenza in dairy cows and the risk to humans
Why is H5N1, or bird flu, a concern, how does it spread, and is there a vaccine? Here are the answers to some frequently asked questions about avian influenza.
'I was scared': Ontario man's car repossessed after missing two repair loan payments
An Ontario man who took out a loan to pay for auto repairs said his car was repossessed after he missed two payments.
opinion The special relationship between King Charles and the Princess of Wales
Royal commentator Afua Hagan writes that when King Charles recently admitted Catherine to the Order of the Companions of Honour, it not only made history, but it reinforced the strong bond between the King and his beloved daughter-in-law.
Charlie Woods, son of Tiger, shoots 81 in U.S. Open qualifier
Charlie Woods failed to advance in a U.S. Open local qualifying event Thursday, shooting a 9-over 81 at Legacy Golf & Tennis Club.
$70M Lotto Max winners kept prize a secret from family for 2 months
During a special winner celebration near their hometown, Doug and Enid shared the story of how they discovered they were holding a Lotto Max ticket worth $70 million and how they kept this huge secret for so long.
Courteney Cox says her partner Johnny McDaid once broke up with her in therapy
Courteney Cox's longtime partner Johnny McDaid once broke up with her in a therapy session.
Are Canadians getting sick from expired food?
A new survey by Dalhousie University's Agri-Food Analytics Lab asked Canadians about their food consumption habits amid rising prices.
Body of Quebec man who died in Cuba found in Russia, family confirms
A Montreal-area family confirmed to CTV News that the body of their loved one who died while on vacation in Cuba is being repatriated to Canada after it was mistakenly sent to Russia.
Documents reveal Ottawa's efforts to get Loblaw, Walmart on board with grocery code
It was evident to the federal government as early as last fall that Loblaw and Walmart might be holdouts to the grocery code of conduct, jeopardizing the project's success.